Restore Vitality & Health
Watch Video and Schedule Your Appointment Today
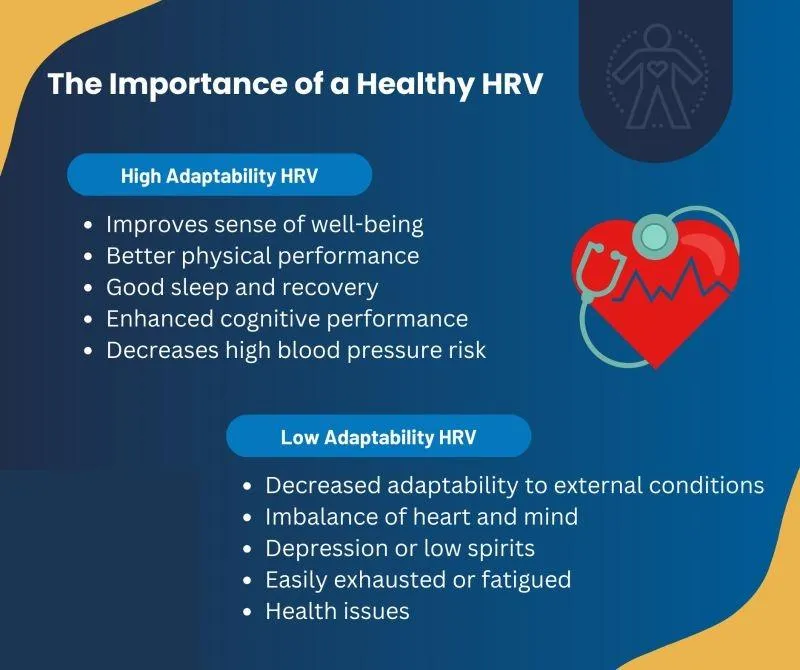
Key points about a healthy HRV
Stress management: Higher HRV suggests better ability to handle stress by effectively switching between the "fight or flight" (sympathetic) and "rest and digest" (parasympathetic) nervous system states.
Cardiovascular health: Studies link low HRV to increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks and arrhythmias.
Mental well-being: A healthy HRV is often associated with better mood regulation and reduced symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Performance optimization: Athletes can use HRV to monitor training load and identify potential overtraining by observing fluctuations in their HRV
Lifestyle insights Tracking your HRV can provide valuable information about how lifestyle factors like sleep, nutrition, exercise, and stress management impact your overall health